Multi-dwelling unit (MDU), namely multi-family residential, are the structures of housing where there are more than one living unit per location. MDU classification of housing has been considered as an important growth opportunity for communication services providers according to the population density and economics of scale. Generally speaking, there are two applications for MDU FTTx network deployments as “greenfield” and “brownfield”. This post will introduce the basic information about MDU and its network building applications.
Three Types of MDUs
In North America, MDUs can be classified into three construction versions of high-rise MDU, mid-rise MDU and low-rise MDU. Here will explain them one by one.
High-Rise MDU
This type of MDU refers to the large multi-story building like condo or apartment with more than ten floors and 128 living units using the internal residential entry. High-rise MDU is typically designed as vertical living style and planned for cabling access to the different stories and sections of the building thereby making sure that the FTTP network functions efficiently and reliably over high levels.

Mid-Rise MDU
Mid-rise (medium-rise) MDU is the leased or owned condo or apartment with up to 10 stories including 12 to 128 living units using the internal residential entry. For new mid-rise MDU, its fiber deployment is similar to the high-rise buildings. However, many old mid-rise MDUs are built as walk-ups and without provisions for new cabling networks. It is a challenge for these mid-rise residential buildings to find space for structured cabling.

Low-Rise MDU
Low-rise MDU is usually known as condo, townhouse or apartment constructed in garden style or horizontal style. There is only up to 3 floors or stories and 12 living units inside the low-rise MDU with external residential entry. The difficulty level for cable deployment also depends on whether the building is newly constructed.

Brownfield and Greenfield Applications
As mentioned above, the oldness and newness of residential buildings will affect the difficulty degree of cable installations. These two types of architectures are also the basic applications for building MDU network. Greenfield means the newly-built housing communities consisting of many separate living units typically joined together in one or several buildings. However, brownfield refers to the MDU that already exists in a typical urban area.
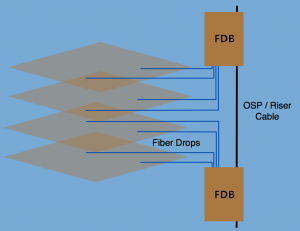
In a Brownfield application, a service provider must deliver fiber into the customer’s premises quickly, efficiently and securely. The ability to connect fibers as they are needed for new subscribers is best served using a simple “plug and play” approach. Thus, the splice storage should provide a demarcation point, such as a fiber demarcation box, equipped with industry standard connectors.
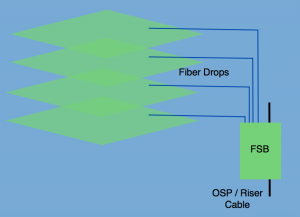
As for greenfield application, a network operator could ideally place the fiber to every living unit during initial construction. Fiber from every unit may then be run back to central closet and spliced as required inside a closure. A box such as the fiber splice box is an optimal and low cost solution.
Fiber Connectivity Methods
In MDU network applications, service providers can use factory-terminated patch cords or fusion-spliced pigtails to connect fibers. Patch cords are efficient connectivity methods because no tools or splices are required in the field to make the termination. Their simple plug and play installation also minimizes the required skills for setting up the connection, which reduces installation time and labor costs.
Fusion-spliced pigtails can alleviate the issues of cable management for massive patch cords and cable waste for long patch cords. However, the fusion splice machine is expensive and specialized training is required. The fusion splicer also requires electrical power in places like MDU hallways where power outlets aren’t readily available.
Conclusion
The building of FTTx network in MDUs has become more and more popular around the world. Project installer should make proper connectivity plan according to different structures of MDUs. The complexity of deployment will also depends on whether the MDU is built in greenfield or brownfield. A successful network deployment in MDU is measured in many ways.
没有评论:
发表评论