Different cables have particular applications. Some are used for data transmission like fiber optic cable or copper cable, and some are used for the transmission of electrical power. Power cord is the assembly widely used as the connection between main electricity supply and the device through a wall socket or extension cord. Power cord is adopted in almost every where when the alternating current power is required. However, have you chosen the right type of power cord for your device? From this article, you may find the answers.
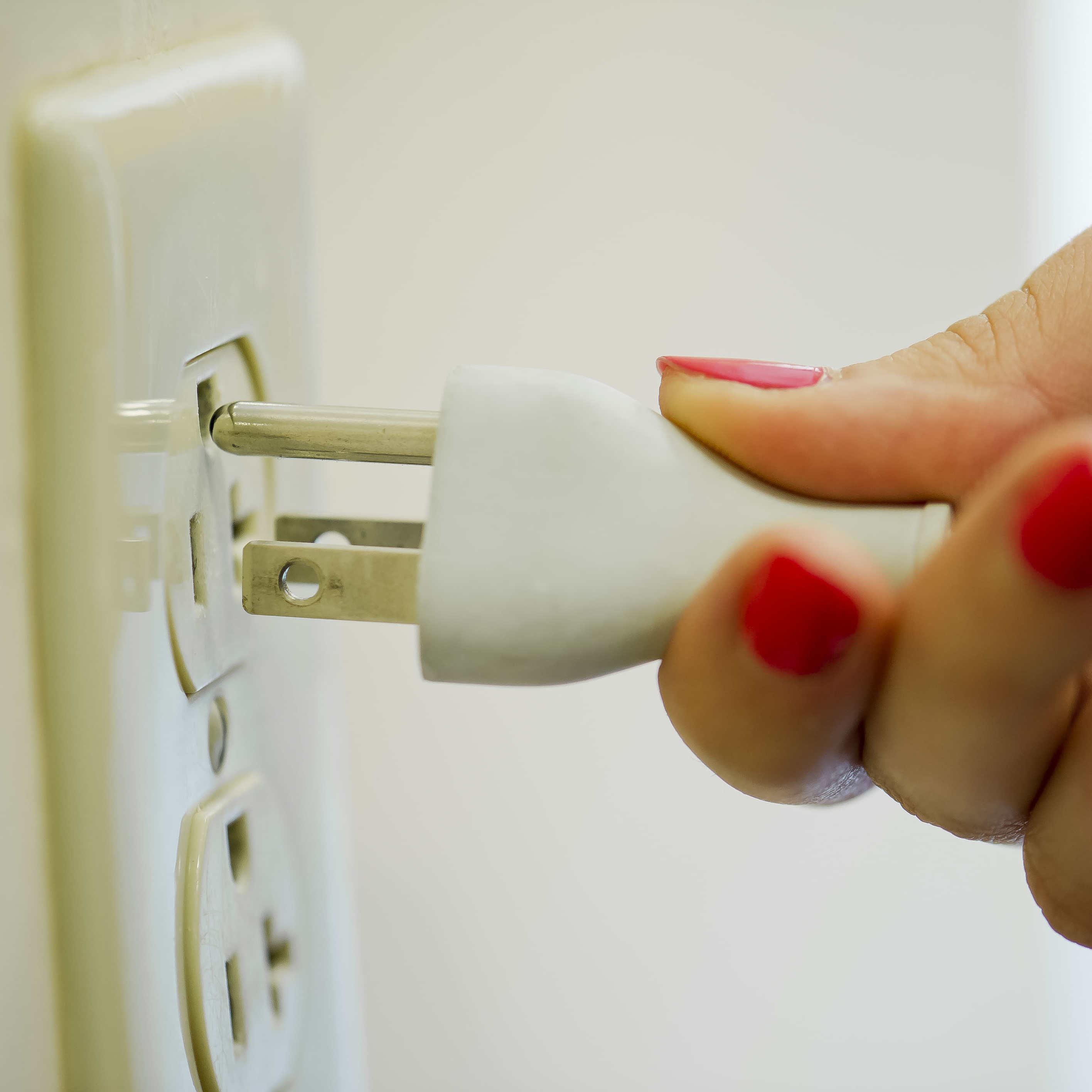

Overview of Power Cord
A power cord set usually has connectors molded to the cord at each end, thus both ends can detach from the power supply and device. Specifically, power cord assembly consists of three major parts. First is the cable plug, and it is also a male connector used for inserting into the AC outlet to provide power. Then is the receptacle on the other end. Receptacle part is also known as the female connector attached to equipment. Cord is the main section that contains the insulated wires with different lengths and thicknesses.
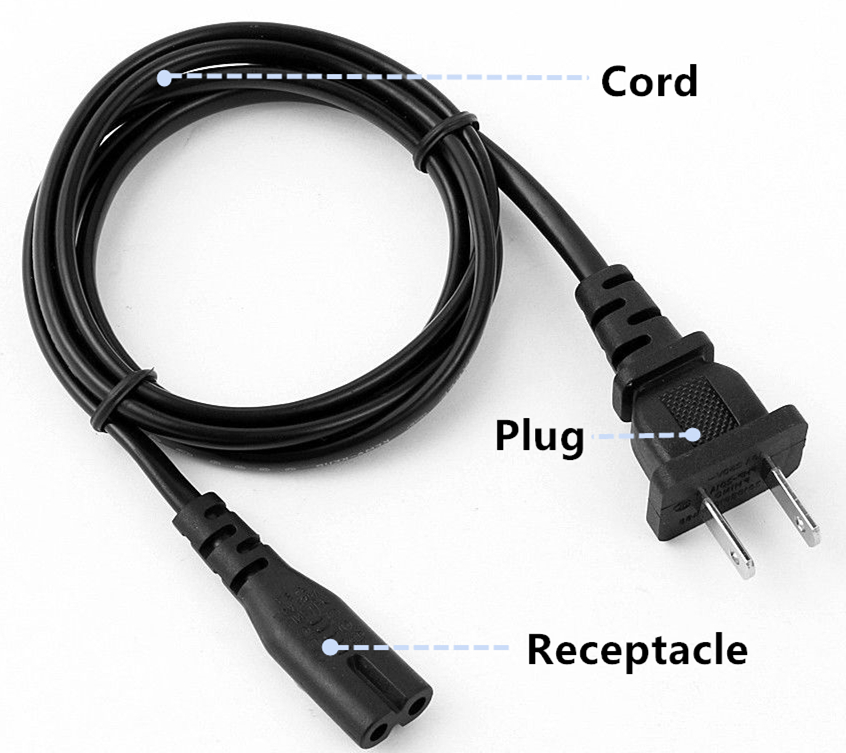

Common Types of Power Cord
According to different plug and receptacle styles, power cords have different standards. In North America, NEMA power cords and IEC 60320 power cords are the common types with the standards set by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). Let’s have a look at their differences.
NEMA Power Cord
NEMA power cords have two series of NEMA 5 and NEMA 6. NEMA 5 series is the type widely found in the United States. It has three-wire circuits (hot, neutral, and ground) and is rated to carry a maximum of 125 volts although usually carries about 110 volts and are referred to as “110 circuits”. NEMA 6 series connectors are used for providing heavy duty power to a device. These are typically 208 volt or 240 volt circuits and often referred to as “220 circuits”.
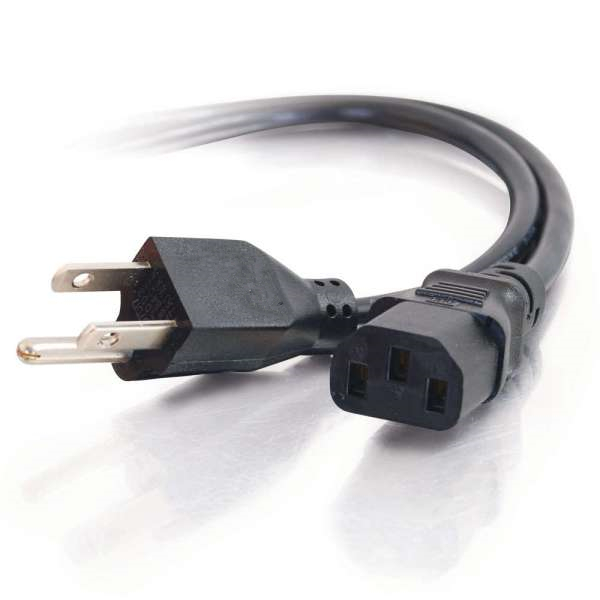

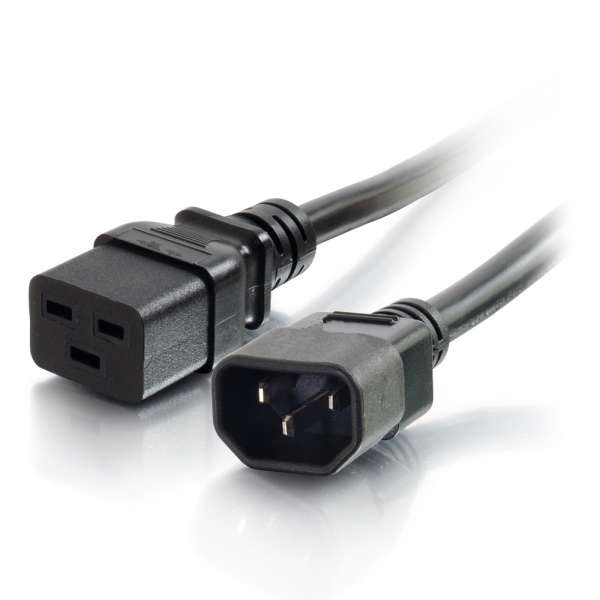
IEC 60320 Power Cord
The ends of IEC 60320 power cord are on the opposite side of the cord from the power plug. To make it an international standard, the equipment manufacturers need to put one kind of receptacle on their equipment and then manufacture the various country-specific cords when needed. The IEC 60320 C13/C14 connector type is seen on most personal computers and monitors. C19/C20 connector type is used for devices like servers and UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems.

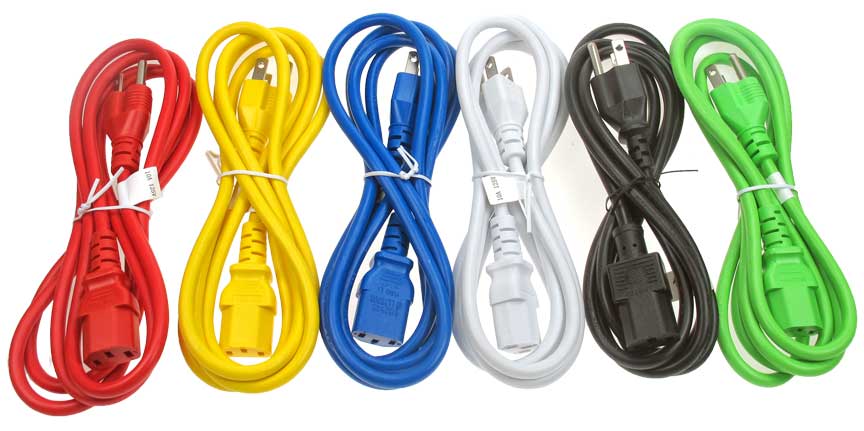
How to Organize Power Cords?
Just like other types of cables, too many power cords can also be easily mixed up during work. Fortunately, there is a simple way to organize the power cords. Instead of labeling all the power cords, you can buy the colored cords for identification. For example, red power cords can be used for important device, and green or blue cords can be used for constantly rearranged equipment. Color coding the system is definitely a more efficient way for cable management.

Conclusion
The standardization of power cords provides great help for the convenient connectivity when powering different kinds of devices. There is usually a long list of power options for the switch or server. You might be confused when all the components are using the acronyms you don’t know. Therefore, understanding the standards can make the selection of power cords much easier.